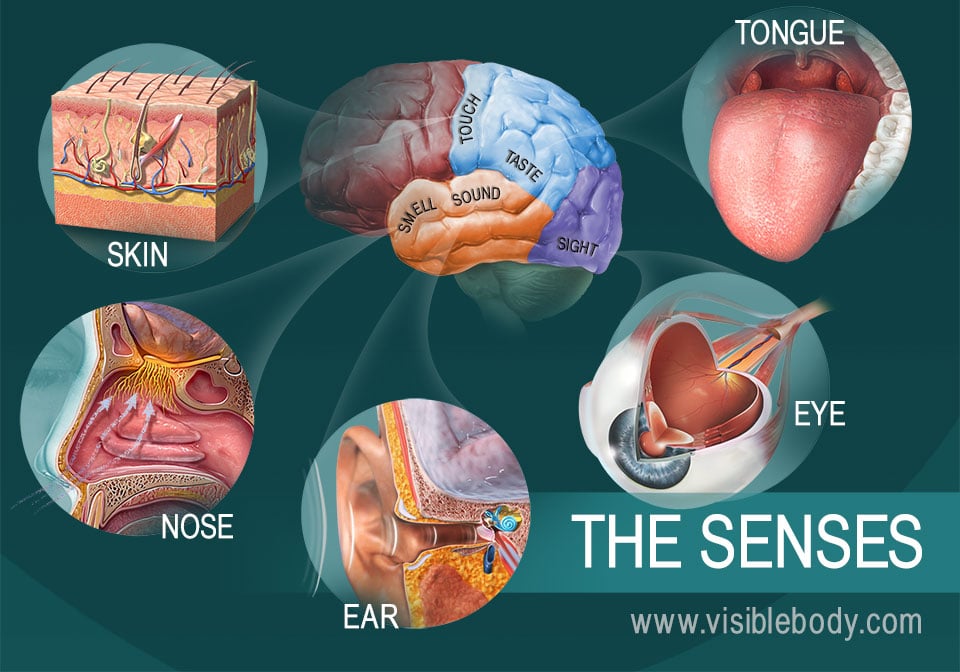
Describe the Sensory Organs of Smell
The cilia trap odour molecules as they pass across the epithelial surface. The thousands of olfactory receptors receptors for the sense of smell occupy a postage stamp-sized area in the roof of each nasal cavity.

The Sense Of Smell Structures That Serve The Sense Of Smell Senses For Kids Youtube
Smell also called olfaction the detection and identification by sensory organs of airborne chemicals.
. Also a component of the respiratory system it. The olfactory receptor neurons are located in a small region within the superior nasal cavity Figure 1521. Cavity divided by the nasal septum into left and right passages.
The taste receptors are specialized cells that detect chemicals present in quantity in the mouth itself. Smell The ability to detect the smell which is close to related to the sense of taste and it is also known as olfaction. The nose is an olfactory organ.
Our olfactory system helps us to perceive different smells. The olfactory epithelium found within the nasal cavity contains olfactory receptor cells which have specialized cilia extensions. The nasal mucosa features four separate olfactory areas.
A nostril is one of the two channels of. The sense of smell or an olfactory sense enables us to detect pleasant unpleasant or odourless things. The receptors for taste and smell are classified as chemoreceptors as these respond to special chemicals in aqueous solution.
In each case the chemicals must go into solution in the film of liquid coating the membranes of the receptor cells before these can be detected. Taste and smell are separate senses with their own receptor organs yet they are intimately entwined. This combinatorial coding allows us to detect many more smells than we have specific receptors.
Start studying 17-1 Describe the sensory organs of smell trace the olfactory pathways to their destinations in the brain and explain the physiological basis of olfactory discrimination. Evaporation of the air with chemicals or. The sense of smell is also known as olfaction.
Like taste the sense of smell or olfaction is also responsive to chemical stimuli. Tastants chemicals in foods are detected by taste buds which consist of special sensory cells. The olfactory cells tend to line the top of the nasal cavity.
This region is referred to as the olfactory epithelium and contains bipolar sensory neurons. It is a cavity that extends from the nostrils to the back of the throat or pharynx. This article describes about the functioning of the various sense organs like the gustatory system olfactory system somatosensation Proprioception and Kinesthesia.
The sense of smell or olfactory sense occurs in olfactory epithelium that occupies a small area on the roof of the nasal cavity. The olfactory receptor cells are bipolar neurons whose dendrites have terminal knobs with hairlike cilia protruding beyond the epithelial surface. Structures of the olfactory system include.
When stimulated these cells send signals to. Each olfactory sensory neuron has dendrites that extend from the apical surface of the epithelium. Perceiving smell begins with olfactory receptors in the nose and ends in the brain.
The chemicals sense of taste and smell are functionally similar and interrelated. This is the ancient part of the brain that is responsible for memory emotions and behaviour. Some scientists think of the limbic system as the central part of the brain that emotionally makes decisions before we realize it.
The concept of smell as it applies to humans becomes less distinct when invertebrates and lower vertebrates fish and. The olfactory receptor cells are neurons equipped with olfactory hairs long cilia that protrude from the nasal epithelium and are continuously bathed by a layer of mucus secreted by underlying glands. The olfactory receptors in the nose act as the sensory organ to sense the smell of chemicals from food or floating in the air.
It is also the first organ that helps in the process of respiration. Ultimately messages about taste and smell converge allowing us to detect the flavors of food. The part of the nose through which air enters is called nostril.
This sense of organ also aids our sense of taste. The sense of smell is very closely related to the work of the limbic system of the brain. It is lined with mucosa.
The nose serves as the entrance to the respiratory tract and contains the olfactory organ. Each smell activates a specific combination of olfactory neurons which the brain decodes as a particular aroma. It is the gateway through which air enters the human body.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Opening containing nasal passages that allows outside air to flow into the nasal cavity. It also conditions the air by filtering warming and moistening it and cleans itself of foreign debris extracted from inhalations.
Olfaction by air-breathing vertebrates depends primarily on chemically sensitive nerves with endings in the lining epithelium smell sense Britannica. The nose is a vital organ of the human body which is responsible for the sense of smell. A detailed coverage is provided on their anatomy types and the functions which each part of these sense organs perform while transmitting the neural messages to the brain.
Our sense of smell is a chemosensory mechanism that detects chemicals in the air via the nose sensory organ. The cilia or olfactory hairs initiate an action potential when they react with a molecule from an inhaled. Olfactory epithelium Lamina propria Olfactory Discrimination-Can distinguish thousands of chemical stimuli-CNS interprets smells by the pattern of receptor activity.
Olfactory Organs-Provide sense of smell -Located in nasal cavity on either side of nasal septum-Made up of two layers. Main olfactory epithelium MOE septal organ SO ganglion of Grüneberg GG vomeronasal sensory epithelium VNsE forms a part of the vomeronasal organ VNO.

Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs

How Flowers Affect Our Senses Senses Infographic Sensory System

The Traditional Five Human Senses And Sense Organs Classroom Lesson Plans My Five Senses Senses Preschool
0 Response to "Describe the Sensory Organs of Smell"
Post a Comment